Object detection is a fundamental task in computer vision that involves identifying and locating objects within an image or video. Unlike image classification, which only labels an image as containing a certain object, object detection also provides the exact position of each object in the form of bounding boxes. This allows systems to not only recognize what is present in a scene but also understand where each object is situated. Common applications of object detection include facial recognition, autonomous driving, medical imaging, and security systems.
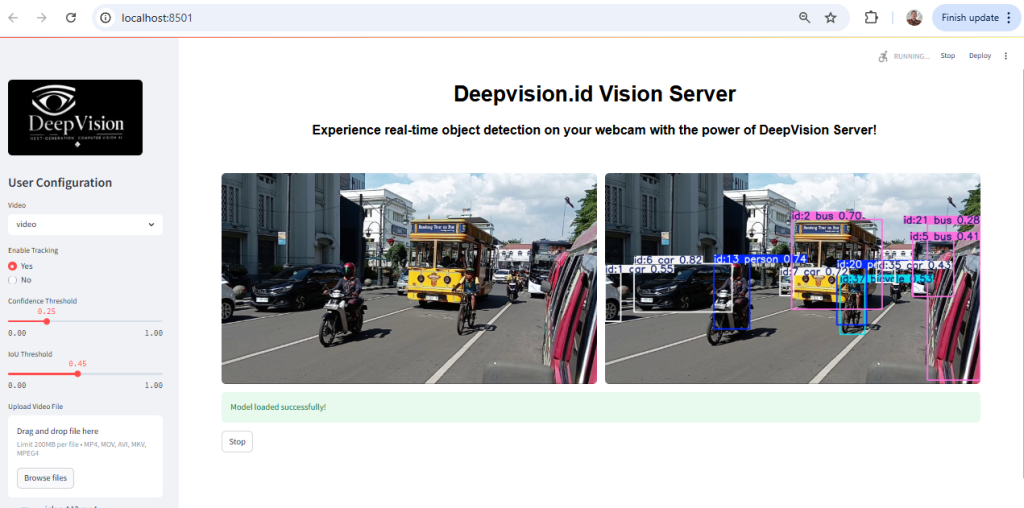
Modern object detection techniques often rely on deep learning, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), to automatically learn features from data. Popular models such as YOLO (You Only Look Once), SSD (Single Shot MultiBox Detector), and Faster R-CNN have achieved significant success in detecting multiple objects in real-time with high accuracy. These models are trained on large datasets to recognize a wide range of object classes. However, challenges still exist, such as detecting small, overlapping, or occluded objects, especially in dynamic and complex environments. Continuous improvements in algorithms and computational power are making object detection increasingly robust and efficient.